In previous post it mentioned that the sensors have digital and analog outputs, however sensors also may have serial outputs, which can send digital, analog signal or both.
Digital output
An important aspect to consider is the type of output and voltage levels. In the sensors with discrete output levels the more common voltages are 24Vdc, 120Vac and 220Vac. The types of outputs are:
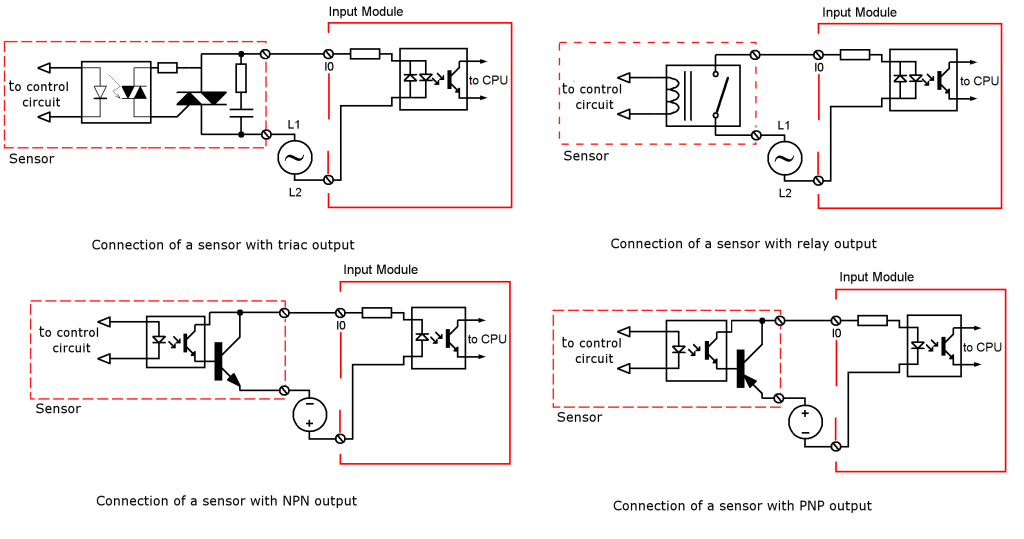
Relay: The relay outputs handle AC and DC voltages up to 240 volts, the output current is in the order of amps, 5 A is a typical value. They are used in general purpose applications, they are inexpensive. They have a long response time (15 ms to open contacts, 25 ms to close the contacts). The outputs of multiple sensors can be wired in series or parallel. Its main disadvantage is the wear suffered by mechanical contacts and sizzle.
Transistor: handle voltages from 0-30 V DC, the output current is in the order of mA (100 mA typical). It has a low leakage current. Response times are short, 1ms or less. They are used for general purpose operating DC.
Triac: the output voltage is 120 or 240 V AC, output current usually is about 0.75 A maximum, has a long response time (8.3 ms to enable or disable). It has a leakage current about 1 mA. They are used in general purpose applications in AC operation. Suitable for inductive loads.
FET: The output voltage is 0-120 V AC or 10-200 V DC, output current is on the order of tens of mA, has short response time (1ms or less), the leakage current is in the order of uA. The outputs of multiple sensors can be wired in series and / or parallel.
MOSFET: the output voltage is 0-120 V AC or 10-200 V DC, output current is on the order of hundreds of mA. The leakage current is moderately high. The outputs from multiple sensors can be wired in parallel.
Analog Outputs
The most widely used standards are current analog 4 to 20 mA and voltage of 0-10 Vdc. There are others like 1-5 VDC, 0-20 mA and 20mA -20mA.
Serial Outputs
The sensors with serial outputs are connected to networks for field devices and the information is serially transmitted (bit stream) through a cable network and sending data from the sensor to the controller or supervision by a communications port. Examples of field bus (field networks) mentioned below: Devicenet, Profibus dp, Foundation FieldBus and in recent years it has increased the functionality of EtherNet/IP as a network of field.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a field bus?
Some advantages and disadvantages of field bus are mentioned below.
Advantages
- Field networks allow reducing the use of digital inputs and outputs wired to the controller and this result in a decrease in cables for connection.
- The serial devices have the advantage over devices with digital and analog outputs that can send more information, which allows equip them with some additional capabilities such as: diagnosis and logical functions (timer, counter and motion detection). These features can reduce maintenance time and allow some of the control logic resides on the sensor.
- The installation cost is reduced when the number of field devices is significant.
- Easier expansion
- Shorter commissioning
Disadvantages
- Better trained staff.
- Additional cost in maintenance tools.