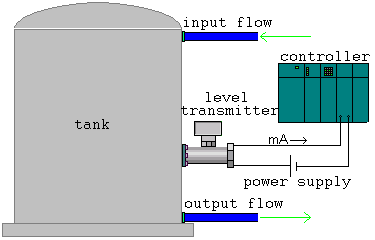
The analog variables are measured with transmitters, for example, if it wants to measure the tank level, it install a level transmitter that provides an analog signal, which, in the most case, it is voltage or current. The next figure shows a level transmitter connected to 2-wire.
Analog Transmission
Some characteristics of the transmitter outputs are shown below:
Voltage Analog Transmission
- It is used for short distances.
- The error is increased when it is increased the length cable.
- The ranges most used are: 0 a 5, 1 a 5 y 0 a 10 Vdc
- The load must be greater to 1KΩ
Current Analog Transmission
- The most used range is 4 a 20 mA.
- The faults in the system are verified in natural way.
- It can be transmitted to distances greater to 3.200ft.
- The load can be between 0 and 1000Ω.
- It has higher immunity to noise that voltage transmission.
- The signal does not degrade with the distance.
Scaling.
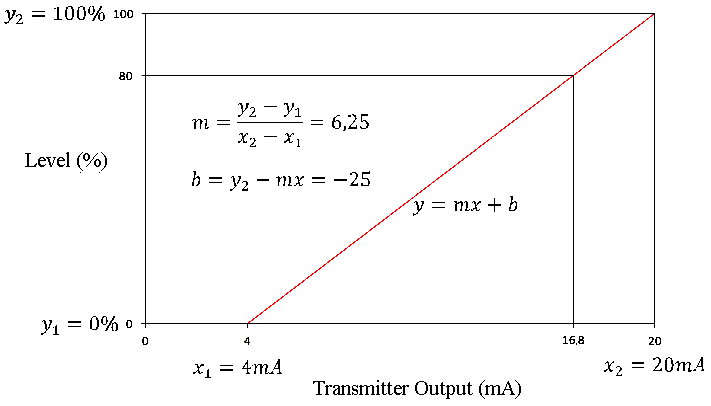
The input or output of the transmitter can be known by using scaling. The scaling allow converting a signal into a range to a different range, this is done to find the relationship between the input and the output of the transmitter. The most transmitters are lineal, for this reason, the corresponding equation is the straight line equation. In the example of the tank, if the transmitter has an output equal to 16.8 mA (range 4 to 20 mA is supposed) and it wants to find the level in percentage (in the range between 0 and 100%) the corresponding value would be 80%, as it is shown in the next figure.
Scaling